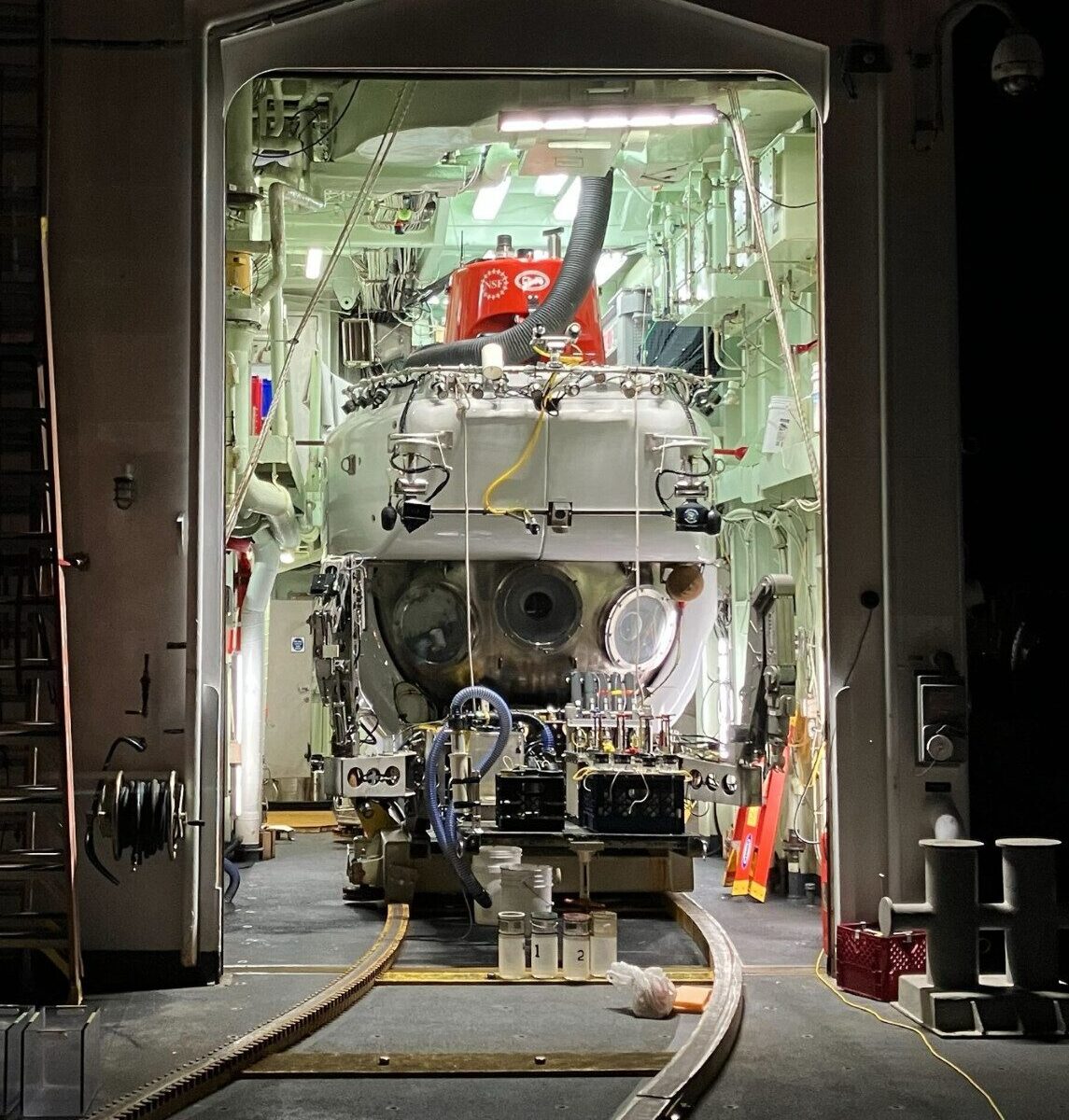
Imagen principal: Alvin – un vehículo de ocupación humana (VOH) sumergible diseñado para permitir la recolección de datos a profundidades hasta 6,500 m por debajo de la superficie del océano. Imágen principal cortesía de John Magyar, Caltech.
Autores: Daniela Osorio-Rodriguez, Kyle S. Metcalfe, Shawn E. McGlynn, Hang Yu, Anne E. Dekas, Mark Ellisman, Tom Deerinck, Ludmilla Aristilde, John P. Grotzinger, and Victoria J. Orphan
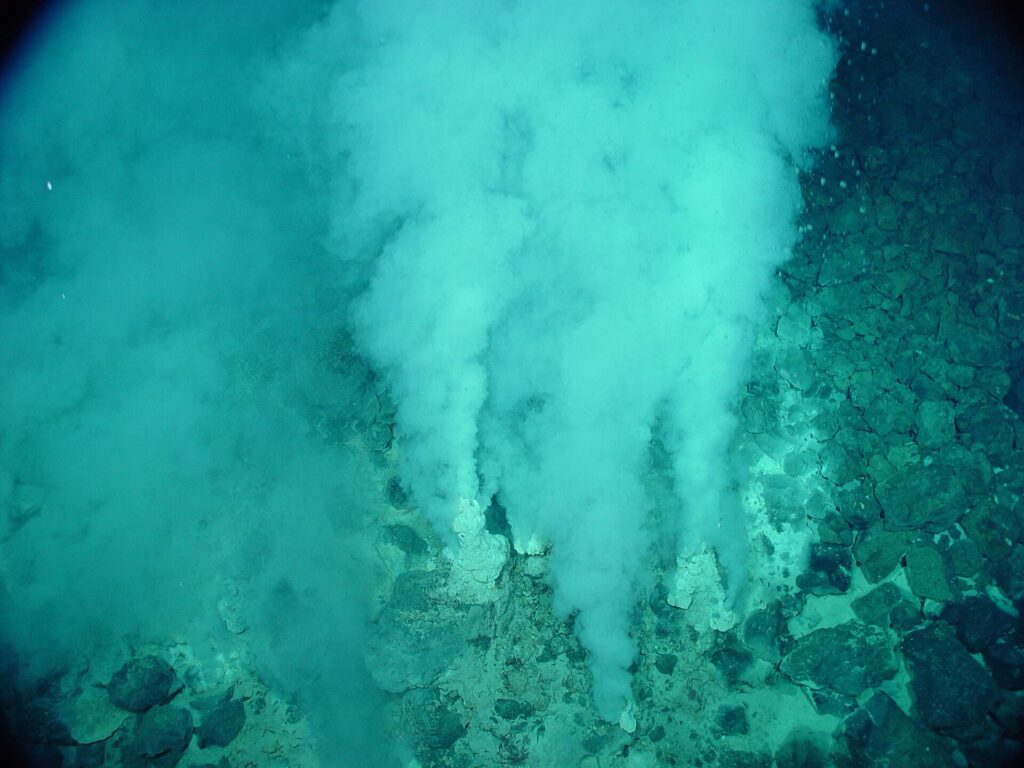
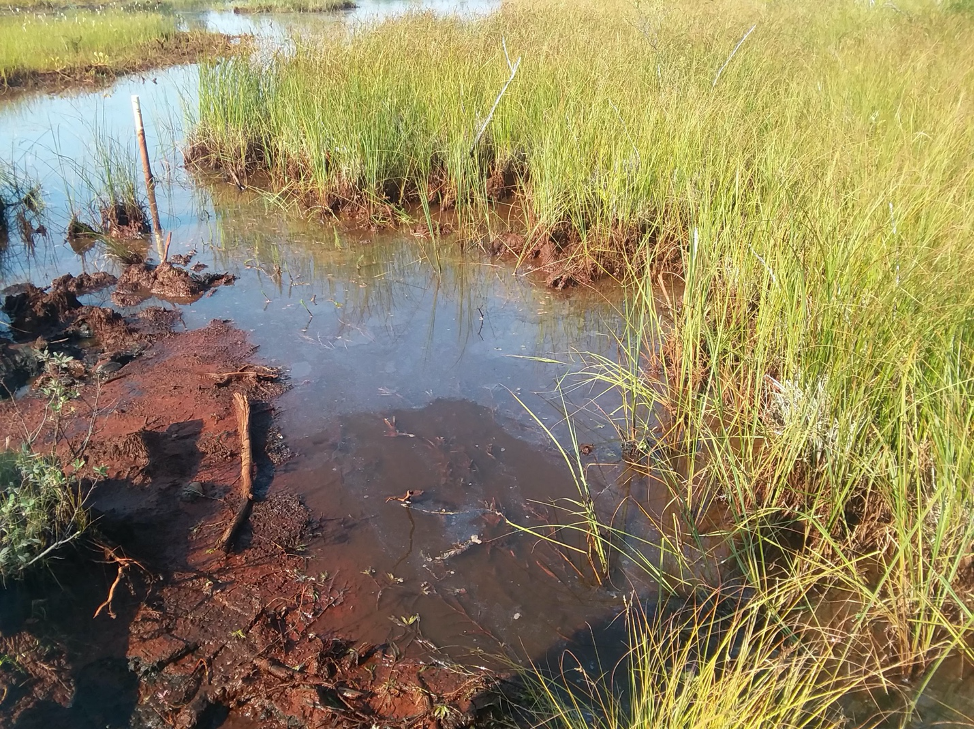
Tal vez un fin de semana en tu vida, te encuentres apilado en un vehículo todoterreno a las 6 de la mañana con otros siete estudiantes, registrando intermitentemente el dron de un profesor de geología demasiado entusiasta cuya clase tomaste para llenar un requisito de tu programa. Si es así, en ese vehículo con certeza se pronunció la proclamación “el presente es la clave del pasado”. Un estudio reciente conducido por Daniela Osorio-Rodriguez y colaboradores epitomiza el poder de esas palabras.
Continue reading “Podemos encontrar microorganismos del mar profundo reposando en tumbas que ellos mismos construyeron”