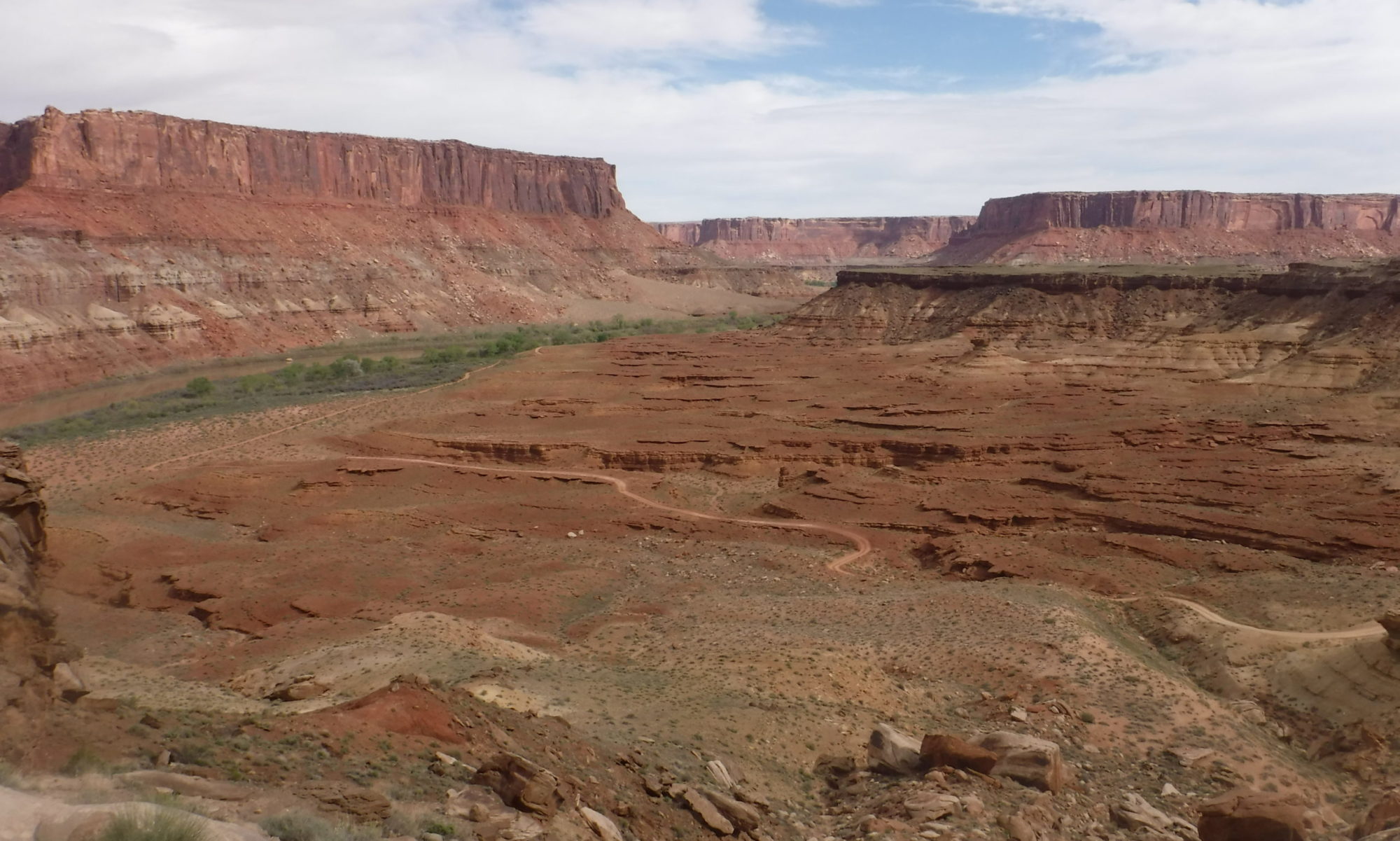
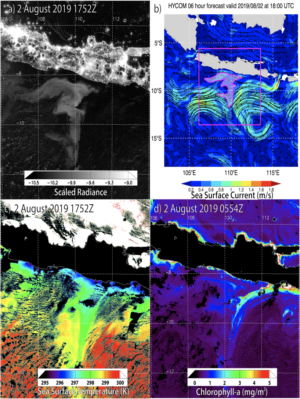
Featured image: Processed satellite images showing a milky sea event and its components in Java, 2019. From Miller et al, 2021 (figure 5).
Sailors see a lot of, well, stuff while they’re far from land. And they’re known for telling unbelievable tales, some of which later turn out to be more or less true. Milky seas are one of those: a horizon-to-horizon sea that glows white like the snow in the moonlight. In a 2021 paper, Dr. Steven Miller of Colorado State University and colleagues used satellites to look for these systems in hopes of understanding how and why these glowing patches form.
The first satellite detection of a milky sea event was also the work of Dr. Miller, in a 2005 paper that detected just a single event by combing ships’ logs and satellite archives from the preceding decade. Now, Miller’s research team has refined the algorithm that he’d previously developed for modern satellite records. Today’s satellite technology is better able to ‘see’ these events due to higher resolution of their images and can pick out the bioluminescent glow of microbes in the ocean better than the last generation of satellites.
Continue reading “One Sailors’ Legend Down, Many More To Go – Multiple Milky Sea Events Detected by Satellite”